Grid-Tie Inverters
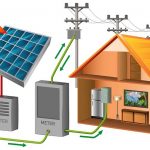
The grid-connected inverter is a special inverter. In addition to converting DC power into AC power, the output AC power can be synchronized with the frequency and phase of the mains power, so the output AC power can be returned to the mains. Grid-connected inverters are commonly used in applications where some DC voltage source (such as a solar panel or a small wind turbine) is connected to the grid.
Advantages of Grid-Tie Inverters
High efficiency. Before the grid-connected inverter generates electricity, it needs to take power from the grid, detect the voltage, frequency, phase sequence, etc. Will be connected to the grid for power generation.
High reliability: When an accident or disturbance in the power system causes a voltage sag at the grid-connected point of the photovoltaic power station, within a certain range of voltage drop and within a certain time interval, the photovoltaic power station can guarantee continuous operation without going off-grid.
The adaptable range of input voltage is wide, not only can be used in rooftop power generation scheme, but also can be used in various small power stations.
How Do Grid-Tie Inverters Work?
When the public grid is powered off, the grid side is equivalent to a short-circuit state. At this time, the grid-connected inverter will be automatically protected due to overload. If the solar battery array has energy output, the inverter will run in the state of independent operation.
Of course, the premise of running alone is that the solar array can provide enough power at that time. If the load is too large or the sunshine conditions are poor, the inverter cannot output enough power, and the terminal voltage of the solar cell array will drop, thereby reducing the output AC voltage and entering the low-voltage protection state. When the power grid is restored, it will automatically switch to the regenerative state.