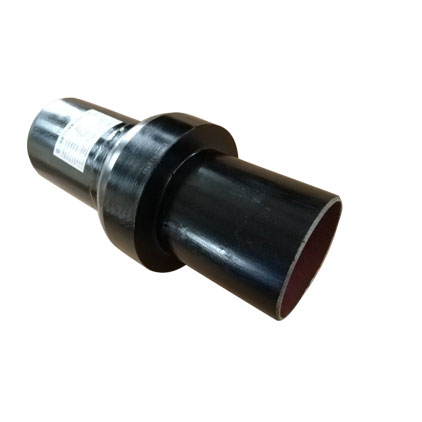
insulating joint
What is an insulating joint?
Insulation joints (or isolation couplings or isolation joints) provide electrical isolation and cathodic protection in pipelines, tanks and pump stations where oil, gas and water are the carrier fluids. Insulation fittings are available in sizes ranging from 2″ to 48″ and pressures ranging from ANSI 150 to ANSI 900.
Three features ensure electrical isolation.
1. insulating gaskets prevent metal-to-metal contact at the joints
2. Internal cavities are filled with a special dielectric compound
3. Inner and outer surfaces are coated with two (2) coats of non-conductive epoxy paint, or according to customer specifications.
The welded end hubs of our insulated joints are supplied according to the customer’s pipe specifications. Optional extra-long stubs (supplied by the customer) can be included in the completed joint.
Features of insulating joints:
1. Non-conductive material: The primary feature of an insulating joint is that it is made of a non-conductive material, which prevents the transfer of electrical current.
2. Easy to install: Insulating joints are typically easy to install, as they do not require any special tools or equipment.
3. Wide temperature range: Many insulating joints are designed to withstand a wide range of temperatures, making them suitable for use in a variety of applications.
4. Chemical resistance: Some insulating joints are made of materials that are resistant to chemical corrosion, which makes them suitable for use in chemical processing plants or other environments where chemicals are present.
The primary advantage of an insulating joint is that it provides electrical isolation between two sections of pipe, which can help to prevent electrical accidents and protect personnel.
Insulating joints are commonly used in a variety of applications, including:
1. Chemical processing plants: In chemical processing plants, insulating joints are used to prevent the transfer of electrical current between pipes, which can help to prevent explosions or other accidents.
2. Oil and gas pipelines: Insulating joints are used in oil and gas pipelines to prevent the transfer of electrical current between pipes, which can help to prevent fires or other accidents.
3. Power plants: Insulating joints are used in power plants to prevent the transfer of electrical current between pipes, which can help to prevent electrical accidents and protect personnel.
4. Water treatment plants: Insulating joints are used in water treatment plants to prevent the transfer of electrical current between pipes, which can help to prevent electrical accidents and protect personnel.
Changhao’s insulating joints feature a prefabricated, non-separable and boltless design to meet the needs of customers who require a single-piece construction to simplify installation, eliminate maintenance and allow for easy final wrapping and coating of the pipe after installation. The design is tested for pressure fatigue, torsion and bending to provide a design that is physically stronger than the pipe it is attached to.
Changhao is fully qualified to provide internal magnetic particle testing, ultrasonic and liquid penetration inspections, and NDE test reports to meet customer requirements. Each of our Changhao is fully factory assembled and hydrostatically tested to 1.5 times the working pressure prior to shipment. In addition, each joint is electrically tested to verify its insulating capability. Insulated joints require no maintenance for their entire service life.