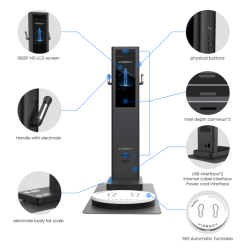
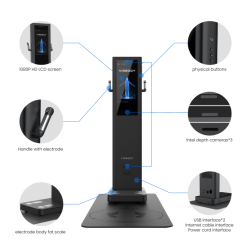
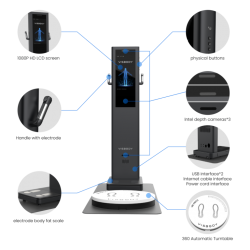
Overview of BIA Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis
The basic principle of the bioelectrical impedance analysis method is that the liquid weight of the cell is closely related to the electrical impedance value, and the total cell water weight and the extracellular water weight can be directly calculated based on the electrical impedance value. However, when the input current frequency is lower than 50 kHz, the current cannot pass through the cell membrane, and only the weight of the extracellular water can be measured at this time; when the current frequency exceeds 200 kHz, the current can pass through the cell membrane, and the total human body can be measured. Moisture, carry out whole body analysis, infer various body composition indexes.
Ⅰ. The BIA bioelectrical impedance analysis is a non-invasive and simple method
The BIA body impedance analysis method uses a weak (not felt by the human body) constant alternating current to measure the electrical impedance of various parts of the human body through the connection of the human hands, feet and electrodes, and conduct a full body composition analyzer of the human body. Human body fat is a non-conductor, while muscle has high water content and is easily conductive. If there is more fat and less muscle, the biochemical resistance value is relatively high when the current is passed, otherwise, the biochemical resistance value is relatively low. Through the above information, it is possible to non-invasively measure the water content, muscle mass, fat content, bone mineral content, etc. inside and outside the body’s cells.
Ⅱ. Factors affecting the effectiveness of BIA bioelectrical impedance analysis
The effectiveness of BIA bioelectrical impedance analysis is affected by factors such as age, gender, disease status, and race. However, its calculation formula uses the five factors that affect the accuracy of weight, gender, height, age, and impedance, which avoids its impact on the measurement results, thereby greatly improving the accuracy of the results.
Ⅲ. The advantages of BIA bioelectrical impedance analysis
1. The BIA is used in the professional body composition analyzer. Using the bioelectrical impedance analysis method can measure 8 kinds of human body components: intracellular fluid, extracellular fluid, total body water, body fat%, protein content, muscle weight, lean body weight, and mineral content, and calculate 11 The indicators are fat percentage, obesity, BMI, basal metabolic rate, standard muscle, standard weight, weight control, fat control, muscle control, target weight, and edema coefficient.
2. The bia body impedance analysis method is reliable as a method of body composition measurement, and its high sensitivity is more suitable for screening children with overweight and obesity. Compared with the skinfold thickness method, the bioelectrical impedance analysis method is more accurate and reliable; and compared with the underwater weighing method, the bioelectrical impedance analysis method has low cost and technical difficulty, is safe and non-invasive, and is suitable for large-scale group research and epidemiology Investigation is of great value for diagnosing obesity or malnutrition and monitoring the nutritional status of patients with chronic diseases.
Ⅳ. Precautions for the BIA bioelectrical impedance analysis method:
1. When using the bioelectrical impedance analyzer, the measurement should be done on an empty stomach. If you have eaten before the measurement, the measurement should be performed at least 2 hours apart. No alcohol is allowed in the 24 hours before the test.
2. Empty your urine and bowels before using the bioelectrical impedance analyzer. If possible, measure in the morning.
3. Please take off your socks before using the bioelectrical impedance analyzer to confirm the correct position of the contact points between the hands, feet and the electrodes.
4. Wear light clothes as much as possible when using the bioelectrical impedance analyzer for measurement, and do not carry heavy items with you.
5. It is not advisable to measure immediately after exercise, stand still for 5 minutes before measuring.
6. Dry or oily skin may prevent the test from continuing.
7. BIA bioelectrical impedance analysis is not suitable to measure immediately after bathing or sauna; it is not suitable to measure women’s menstrual period.
8. It is not suitable for amputation patients; it is not suitable for patients with pacemakers.