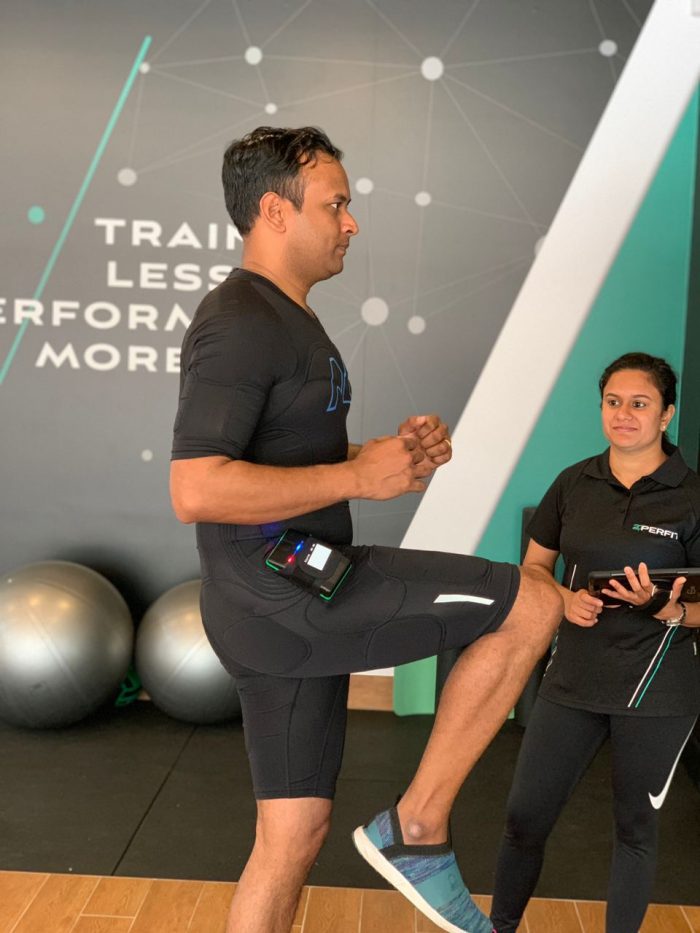
Understanding the Mechanisms of Electric Muscle Stimulation: the Science Behind It.
EMS works by generating electrical signals that imitate the messages sent by the nervous system to the muscles. These signals can be transmitted to the muscles via electrodes that are attached to the skin or through devices that are implanted directly into the muscles.
When an electric signal is sent to a muscle, it prompts the muscle fibres to shorten, which is called contraction. This contraction happens because of the discharge of calcium ions inside the muscle fibres, which initiates a chain of chemical processes that ultimately cause the muscle to contract.
EMS can be used for a variety of purposes, including:
Rehabilitation: Rehabilitation involves the use of EMS (electrical muscle stimulation) to aid in the recovery of patients who have experienced muscle function loss due to injuries or surgeries. EMS works by stimulating the muscles, which can help to prevent muscle atrophy and maintain muscle mass.
Sports training: EMS fitness can be utilized to boost muscle endurance and strength, as well as enhance athletic performance in activities like swimming, running, and cycling.
Aesthetics: Electrical muscle stimulation (EMS) can help to strengthen and tighten muscles, as well as minimize the visibility of cellulite.
To put it briefly, EMS functions by utilizing electrical impulses to imitate the messages transmitted from the nervous system to the muscles.
Our Address: Shop 1, 3 Victoria Road, Parramatta, NSW, 2150, Australia
Google Map: https://g.page/r/CStxK5biCcmXEBM/
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/20perfit/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/20perfit/
Linkedin: https://au.linkedin.com/company/20-perfit
Youtube: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OHUw9f05i5Q
Twitter: https://twitter.com/20perfit